스택(Stack)
스택은 원소의 특정한 순서를 유지하고 특정 연산을 가지고 있는 선형 자료구조이다.
스택은 후입선출의 선형 자료 구조로서, 한쪽 끝에서만 삽입 및 삭제가 수행된다.
나중에 들어간 원소가 먼저 들어온 원소보다 먼저 나간다 하여 후입선출이라 불리게 된다.
스택은 또한 Top이라 불리는 포인터를 가지고 있는데 이는, 스택의 맨 위의 원소를 가리킨다.(그림상)
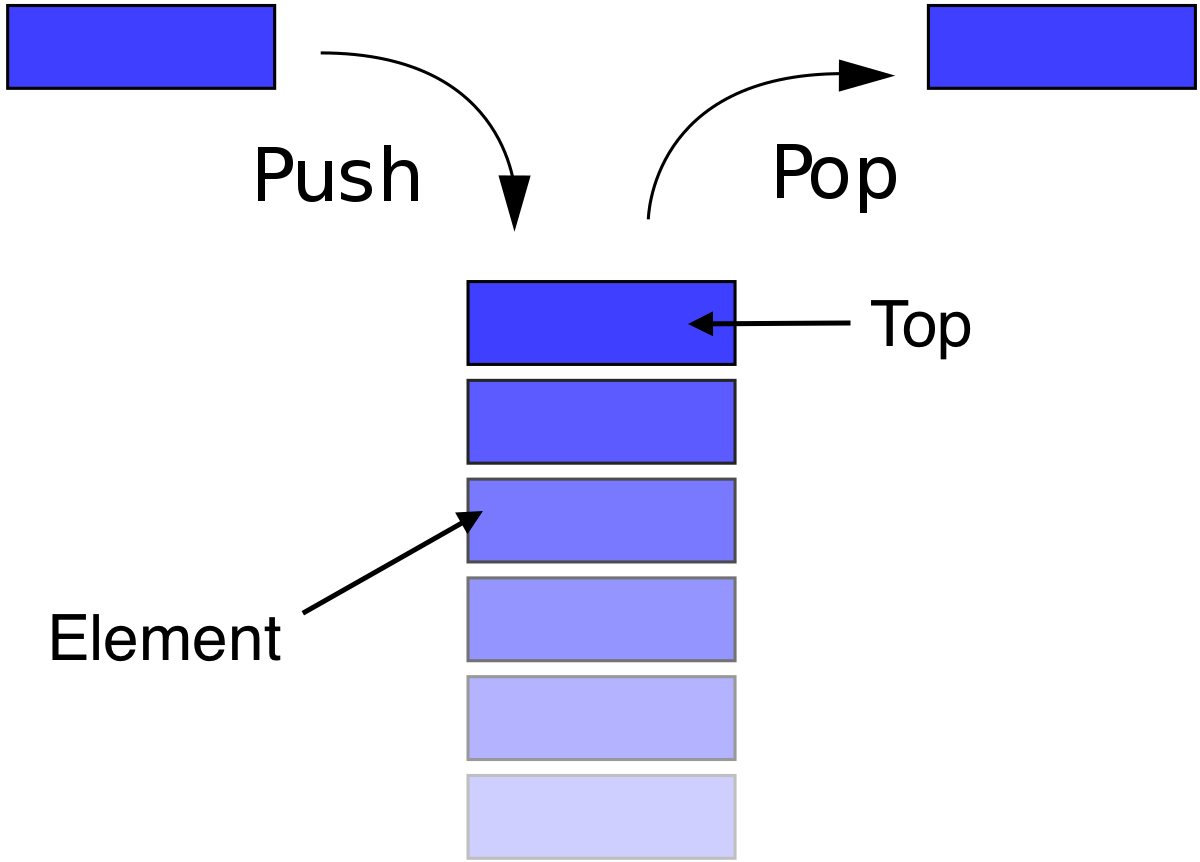
스택의 기본 연산
스택이 가지고 있는 연산들을 보자.
Push
스택에 원소를 삽입한다.
스택이 Full이라면 Overflow 에러가 난다.
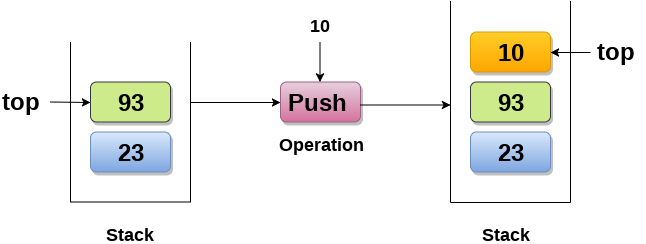
Notice: 새로운 원소가 삽입됨에 따라 Top이 10을 가리키고 있다.
Pop - 스택에서 원소를 삭제한다.
스택에서 원소를 삭제한다.
스택이 빈 공간이면, Underflow 에러가 난다.
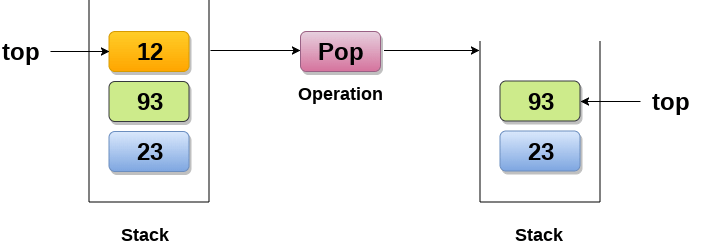
Notice: 기존 원소가 삭제됨에 따라 Top이 93을 가리키고 있다.
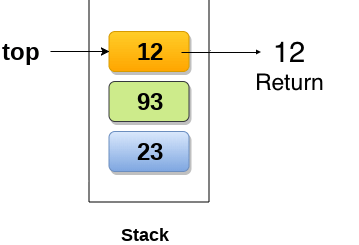
Peek
스택에서 Top 가리키고 있는 원소를 반환한다.
Notice: 원소가 삽입, 삭제 되는 것이 아닌 원소 반환이므로 Top의 위치는 변화가 없다.
isEmpty
스택이 빈 공간이라면 true, 아니라면 false를 반환한다.
스택의 응용
스택은 많은 곳에서 응용되어 쓰인다.
- 괄호의 균형성 검사. ex) (()) 짝이 맞는지
- 웹브라우저의 앞으로 가기 또는 뒤로 가기
- 그래프 알고리즘 중에서 위상정렬이나 강한연결요소
- 대표적 백트래킹 문제 - N-Queen, Knight tour, rat in a maze, sudoku
- 스택을 이용한 여러 알고리즘 문제 - 하노이 탑, 트리순회, 히스토그램 면적 등
- 중위식 표기법의 후위식 표기법으로의 변환
구현
스택을 구현하는 데에는 크게 두 가지 방법이 있다.
- 배열을 이용
- 연결 리스트를 이용
먼저 배열을 이용한 스택 구현을 보자.
배열을 이용한 스택 구현
스택 클래스의 프로퍼티와 생성자
스택의 최대 크기를 결정하는 MAX 상수, top 포인터, 원소를 담을 배열을 선언한다.
스택이 생성되면 top을 -1로 초기화할 생성자를 선언한다.
class Stack {
static final int MAX = 1000;
int top;
int a[] = new int[MAX]; // Maximum size of Stack
public Stack() // Constructor of Stack Class
{
top = -1;
}
}
스택 클래스의 메서드 - push
스택에 원소를 삽입하는 메서드이다.
top이 배열의 끝(MAX-1)을 가리키고 있으면 스택은 다 차서 더 이상 원소 삽입이 안되므로 에러 메세지를 출력하고 false를 리턴한다.
그렇지 않다면 top을 한 칸 올리고 그 자리에 원소를 삽입한다.
boolean push(int x)
{
if (top >= (MAX - 1)) {
System.out.println("Stack Overflow");
return false;
}
else {
a[++top] = x;
System.out.println(x + " pushed into stack");
return true;
}
}
스택 클래스의 메서드 - pop
스택에서 원소를 삭제하는 메서드이다.
top이 0보다 작으면 스택은 빈 공간이므로 에러 메세지를 출력하고 false를 리턴한다.
그렇지 않다면 top이 가리키는 원소를 리턴하고 top은 한 칸 감소한다.
int pop()
{
if (top < 0) {
System.out.println("Stack Underflow");
return 0;
}
else {
int x = a[top--];
return x;
}
}
스택 클래스의 메서드 - peek
스택의 top이 가리키는 원소를 반환하는 메서드이다.
top이 0보다 작으면 스택은 빈 공간이므로 에러 메세지를 출력하고 false를 리턴한다.
그렇지 않다면 top이 가리키는 원소를 리턴한다.
int peek()
{
if (top < 0) {
System.out.println("Stack Underflow");
return 0;
}
else {
int x = a[top];
return x;
}
}
스택 클래스의 메서드 - isEmpty
스택이 빈 공간인지 확인하는 메서드이다.
top이 0보다 작으면 스택은 빈 공간이므로 true 리턴
그렇지 않다면 원소가 있다는 뜻이므로 false 리턴
int peek()
boolean isEmpty()
{
return (top < 0);
}
전체 코드
다음은 배열을 이용하여 스택을 구현한 전체 코드이다.
/* Java program to implement basic stack
operations */
class Stack {
static final int MAX = 1000;
int top;
int a[] = new int[MAX]; // Maximum size of Stack
boolean isEmpty()
{
return (top < 0);
}
Stack()
{
top = -1;
}
boolean push(int x)
{
if (top >= (MAX - 1)) {
System.out.println("Stack Overflow");
return false;
}
else {
a[++top] = x;
System.out.println(x + " pushed into stack");
return true;
}
}
int pop()
{
if (top < 0) {
System.out.println("Stack Underflow");
return 0;
}
else {
int x = a[top--];
return x;
}
}
int peek()
{
if (top < 0) {
System.out.println("Stack Underflow");
return 0;
}
else {
int x = a[top];
return x;
}
}
}
// Driver code
class Main {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Stack s = new Stack();
s.push(10);
s.push(20);
s.push(30);
System.out.println(s.pop() + " Popped from stack");
}
}
Output :
10 pushed into stack
20 pushed into stack
30 pushed into stack
30 popped from stack
연결 리스트 이용한 스택 구현
연결 리스트를 이용한 스택 클래스 표현
스택의 top을 표현할 StackNode 타입의 root 레퍼런스 가지고 있다.
또한, 스택 원소 즉, 노드를 표현할 내부 클래스를 가지고 있다.
내부 클래스인 스택 노드 클래스는 데이터를 담을 data 변수, 다음 원소를 가리키는 next 레퍼런스 변수를 가지고 있다.
public class StackAsLinkedList {
StackNode root;
static class StackNode {
int data;
StackNode next;
StackNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
}
스택 클래스의 메서드 - push
데이터를 받아 노드를 할당한다.
스택이 빈 공간이면 단순히 root가 새로 생성된 노드를 가리키게 한다.
빈 공간이 아니라면 임시 레퍼런스 변수 temp가 root를 가리키게한다.
root는 새로 생성된 노드를 가리키게 하고, 새로 생성된 노드는 temp를 가리키게 한다.
public void push(int data)
{
StackNode newNode = new StackNode(data);
if (root == null) {
root = newNode;
}
else {
StackNode temp = root;
root = newNode;
newNode.next = temp;
}
System.out.println(data + " pushed to stack");
}
스택 클래스의 메서드 - pop
스택이 빈 공간이면 에러 메세지를 출력하고 int 최소 값을 반환한다.
(여기서는 Integer.MIN_VALUE는 빈 공간임을 표시하는 수로 쓰였다.)
빈 공간이 아니라면 popped 변수에 값을 담고, root는 다음 변수를 가리키게 한다.
popped을 리턴한다.
public int pop()
{
int popped = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if (root == null) {
System.out.println("Stack is Empty");
}
else {
popped = root.data;
root = root.next;
}
return popped;
}
스택 클래스의 메서드 - peek
스택이 빈 공간이면 에러 메세지를 출력하고 int 최소 값을 반환한다.
(여기서도 Integer.MIN_VALUE는 빈 공간임을 표시하는 수로 쓰였다.)
빈 공간이 아니라면 root가 가리키는 값을 리턴한다.
public int peek()
{
if (root == null) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty");
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
else {
return root.data;
}
}
스택 클래스의 메서드 - isEmpty
스택이 빈 공간 즉, root가 null이면 true 리턴, 아니라면 false 리턴
public boolean isEmpty()
{
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
전체 코드
다음은 연결 리스트를 이용하여 스택을 구현한 전체 코드이다.
public class StackAsLinkedList {
StackNode root;
static class StackNode {
int data;
StackNode next;
StackNode(int data)
{
this.data = data;
}
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
public void push(int data)
{
StackNode newNode = new StackNode(data);
if (root == null) {
root = newNode;
}
else {
StackNode temp = root;
root = newNode;
newNode.next = temp;
}
System.out.println(data + " pushed to stack");
}
public int pop()
{
int popped = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if (root == null) {
System.out.println("Stack is Empty");
}
else {
popped = root.data;
root = root.next;
}
return popped;
}
public int peek()
{
if (root == null) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty");
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
else {
return root.data;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
StackAsLinkedList sll = new StackAsLinkedList();
sll.push(10);
sll.push(20);
sll.push(30);
System.out.println(sll.pop() + " popped from stack");
System.out.println("Top element is " + sll.peek());
}
}
Output :
10 pushed to stack
20 pushed to stack
30 pushed to stack
30 popped from stack
Top element is 20
스택 연산들의 시간복잡도
시간복잡도 - 최악 기준
push pop peek isEmpty
O(1) O(1) O(1) O(1)

Leave a comment