Queue
큐(queue)는 컴퓨터의 기본적인 자료 구조의 한가지로, 먼저 집어 넣은 데이터가 먼저 나오는 FIFO (First In First Out)구조로 저장하는 형식을 말한다. 영어 단어 queue는 표를 사러 일렬로 늘어선 사람들로 이루어진 줄을 말하기도 하며, 먼저 줄을 선 사람이 먼저 나갈 수 있는 상황을 연상하면 된다.
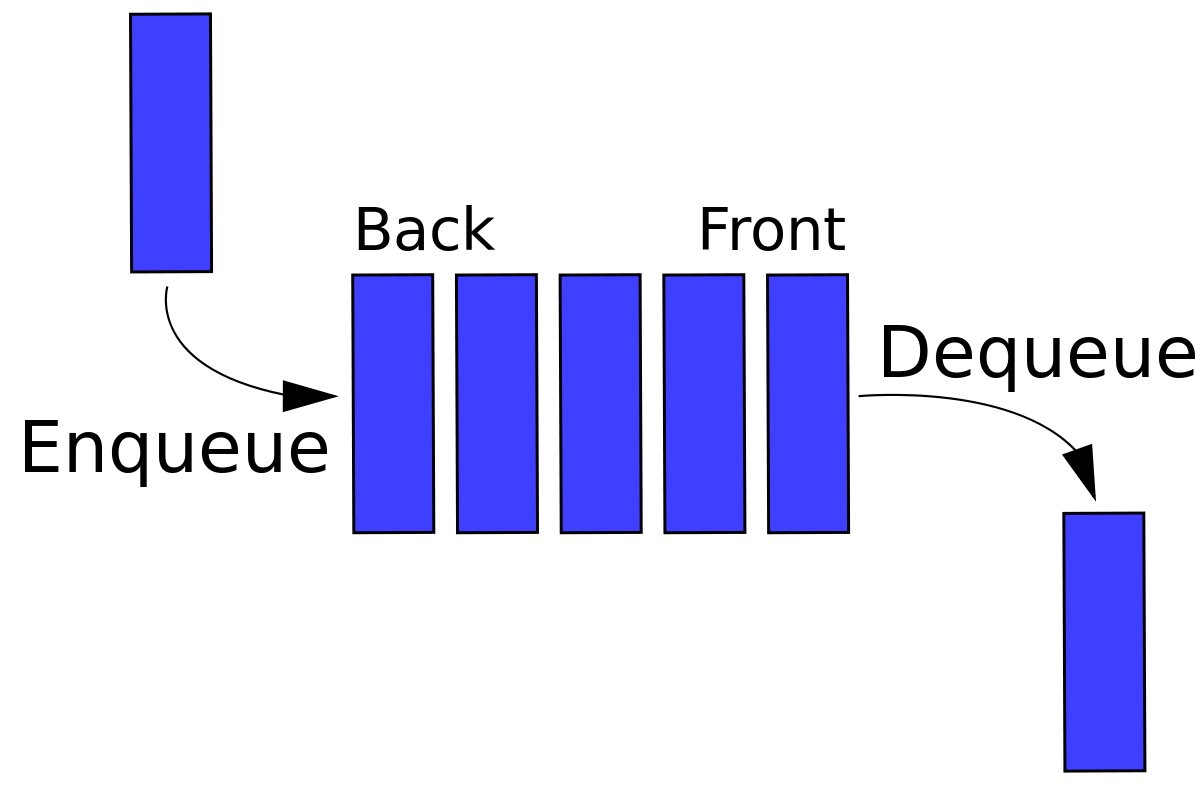
Representation
- Array: 기본적으로 배열을 사용해서 큐를 구현할 수 있다.
- Linked List: 링크드 리스트를 이용하면 배열에 비해 쉽게 구현이 가능하다.
Note: 이번 포스트에서는 자바로 Linked List를 이용해서 큐를 구현해 본다.
Queue Node - 큐 원소를 표현하기 위한 노드 클래스
// A linked list (LL) node to store a queue entry
class QNode {
int key;
QNode next;
// constructor to create a new linked list node
public QNode(int key)
{
this.key = key;
this.next = null;
}
}
Queue Node - 큐를 표현하는 클래스
class Queue {
QNode front, rear;
public Queue()
{
this.front = this.rear = null;
}
}
Note: 큐는 맨 처음 원소를 가리키는 front와 맨 끝 원소를 가리키는 rear 포인터를 가지고 있다.
Operation
큐가 지원하는 연산들을 알아보자.
- Enqueue: 큐의 맨 끝에 원소를 추가하는 연산.
- Dequeue: 큐의 맨 처음의 원소를 삭제하고 반환하는 연산. 큐가 비었으면 null을 반환한다.
Enqueue - 원소 추가 연산
void enqueue(int key) {
// Create a new LL node
QNode temp = new QNode(key);
// If queue is empty, then new node is front and rear both
if (this.rear == null) {
this.front = this.rear = temp;
return;
}
// Add the new node at the end of queue and change rear
this.rear.next = temp;
this.rear = temp;
}
Dequeue - 원소 삭제 연산
QNode dequeue() {
// If queue is empty, return NULL.
if (this.front == null)
return null;
// Store previous front and move front one node ahead
QNode temp = this.front;
this.front = this.front.next;
// If front becomes NULL, then change rear also as NULL
if (this.front == null)
this.rear = null;
return temp;
}
Queue Implementation - 전체 코드
// A linked list (LL) node to store a queue entry
class QNode {
int key;
QNode next;
// constructor to create a new linked list node
public QNode(int key)
{
this.key = key;
this.next = null;
}
}
// A class to represent a queue
// The queue, front stores the front node of LL and rear stores the
// last node of LL
class Queue {
QNode front, rear;
public Queue()
{
this.front = this.rear = null;
}
// Method to add an key to the queue.
void enqueue(int key)
{
// Create a new LL node
QNode temp = new QNode(key);
// If queue is empty, then new node is front and rear both
if (this.rear == null) {
this.front = this.rear = temp;
return;
}
// Add the new node at the end of queue and change rear
this.rear.next = temp;
this.rear = temp;
}
// 큐에서 원소를 삭제하는 연산
QNode dequeue()
{
// If queue is empty, return NULL.
if (this.front == null)
return null;
// Store previous front and move front one node ahead
QNode temp = this.front;
this.front = this.front.next;
// If front becomes NULL, then change rear also as NULL
if (this.front == null)
this.rear = null;
return temp;
}
}
// Driver class
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Queue q = new Queue();
q.enqueue(10);
q.enqueue(20);
q.dequeue();
q.dequeue();
q.enqueue(30);
q.enqueue(40);
q.enqueue(50);
System.out.println("Dequeued item is " + q.dequeue().key);
}
}
Queue q = new Queue();
빈 큐가 생성이 된다.
현재: q = []
q.enqueue(10);
q.enqueue(20);
(10, 20)이 들어온다.
현재: q = [10, 20];
q.dequeue();
q.dequeue();
(10, 20)이 나간다.
현재: q = [];
q.enqueue(30);
q.enqueue(40);
q.enqueue(50);
(30, 40, 50)이 차례대로 들어온다.
현재: q = [30, 40, 50];
System.out.println("Dequeued item is " + q.dequeue().key);
디큐 연산으로 인해 맨앞의 30이 삭제되고 반환된다.
Output: Dequeued item is 30
자바가 제공하는 큐
자바에서는 Queue Interface를 구현한 Linked List Class를 제공한다.
큐 선언:
Queue<T> queue = new LinkedList<T>();
큐 연산:
queue.offer(); // 삽입 연산
queue.pop(); // 삭제하고 원소 반환
queue.peek(); // 큐의 맨 앞 원소 반환
queue.isEmpty(); // 큐가 비었는지 확인
Time Complexity
Algorithm Average WorstCase
Space O(n) O(n)
Search O(n) O(n)
Insert O(1) O(1)
Delete O(1) O(1)

Leave a comment